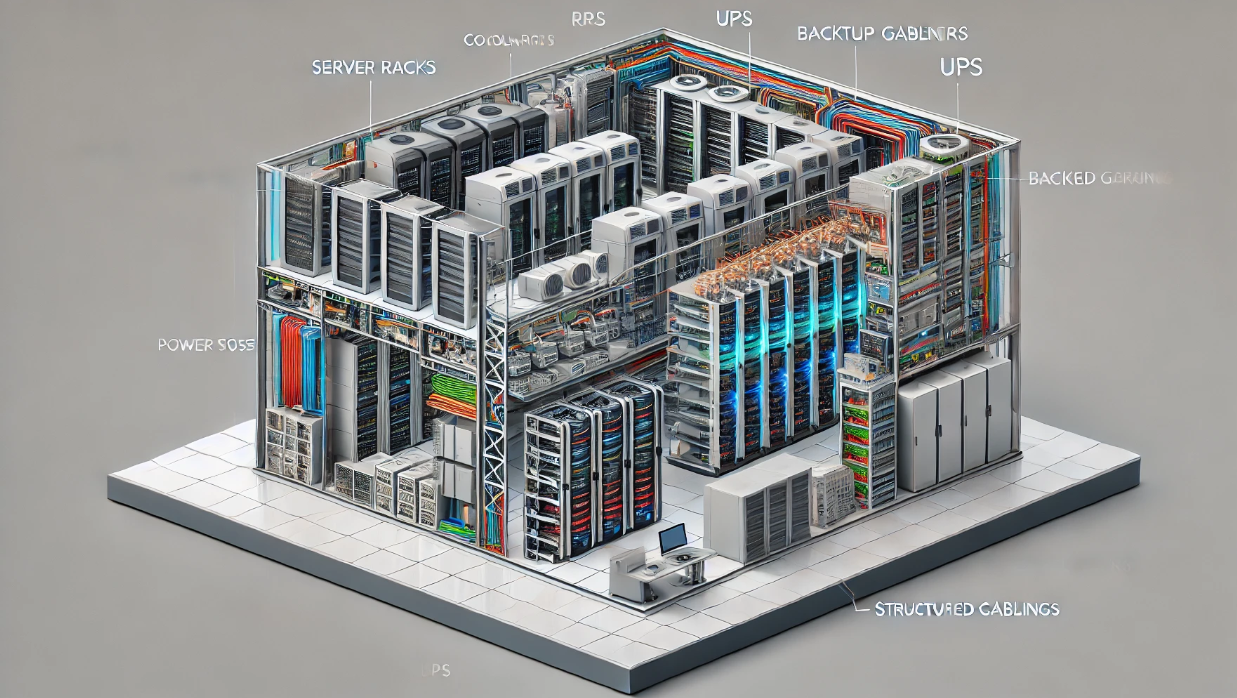
Inside a Modern Data Center: Infrastructure, Cooling, and Power Systems Explained
Meta Description: Step inside a modern data center and explore its architecture, cooling systems, power redundancy, and security. Learn how hosting infrastructure supports uptime, performance, and reliability.
Introduction: The Digital Backbone You Never See
Every website you visit, app you open, or file you upload is powered by a physical data center — a fortress of servers, cables, cooling systems, and power infrastructure.
Modern data centers are highly engineered environments, built for one goal: to deliver fast, secure, always-on access to digital services.
In this post, we’ll take you behind the scenes and explore:
-
How data centers are designed and structured
-
How they stay online 24/7
-
The systems that keep servers cool and protected
Whether you’re hosting a small website or deploying enterprise infrastructure, understanding how data centers work will help you choose the right hosting partner with confidence.
️ 1. Core Infrastructure: The Physical Layers
Modern data centers are more than server rooms. They are multi-layered, controlled environments with the following core components:
️ Server Racks
-
Contain physical servers, switches, and storage devices
-
Organized by row and cabinet
-
Designed with airflow and cable management in mind
Network Hardware
-
Redundant core switches and routers
-
Fiber optic cabling for high-speed interconnects
-
Segmented LANs for security and performance
Storage Arrays
-
Centralized storage (SAN/NAS) for data integrity and backup
-
SSDs and HDDs optimized for IOPS or capacity use cases
Data centers are meticulously organized for performance, maintenance access, and scalability.
️ 2. Cooling Systems: Keeping Servers From Overheating
Servers run hot — and high-density environments can get dangerously warm fast.
Primary Cooling Methods:
❄️ Cold Aisle / Hot Aisle Containment
-
Aligns racks in alternating rows
-
Cold air enters the front, hot air exits the back
-
Prevents hot/cold air mixing
Liquid Cooling
-
Direct-to-chip or immersion cooling
-
More efficient for high-density setups and HPC workloads
️ Free Cooling / Air Economization
-
Uses outside air in cool climates to reduce HVAC load
-
Significantly lowers energy use
⚙️ Efficient cooling protects hardware, lowers costs, and reduces the carbon footprint.
3. Power Systems: Redundancy Keeps It All Running
Downtime is expensive — which is why power systems are the heartbeat of any modern data center.
Key Components:
Dual Power Feeds
-
Two independent power sources from the utility grid
-
Provides failover in case of outage
⚡ UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply)
-
Immediate battery backup for short outages or surges
-
Keeps critical systems online until generators start
️ Backup Generators
-
Diesel or gas-powered
-
Can power the facility for hours or days during grid failure
Power Distribution Units (PDUs)
-
Smart PDUs monitor voltage, current, and load
-
Distribute power evenly to server racks
️ Tier III and IV data centers offer N+1 or 2N redundancy to ensure power continuity.
️ 4. Physical and Network Security
Physical Security:
-
24/7 on-site personnel
-
Multi-layer access controls (badges, biometrics, mantraps)
-
Video surveillance and audit trails
Network Security:
-
Firewalls and intrusion detection systems (IDS)
-
DDoS protection and traffic filtering
-
Segregated VLANs and private peering links
Security isn’t just digital — it’s baked into the facility’s design.
5. Connectivity and Carrier Access
Data centers act as hubs for internet and private network access:
-
Multiple Tier 1 and Tier 2 carriers on-site (multi-homed)
-
Redundant fiber paths and cross-connects
-
Direct peering with cloud providers and CDN networks
Low-latency access is critical for hosting, gaming, streaming, and financial applications.
6. Environmental Control and Monitoring
Modern data centers rely on:
-
Real-time monitoring for temperature, humidity, airflow
-
Leak detection, smoke alarms, and access alerts
-
Automated alerts for power spikes or cooling failures
Monitoring tools integrate with NOC dashboards to allow quick intervention before problems become disasters.
✅ Final Thoughts: The Power Behind the Performance
From the outside, a data center might look like just another industrial building — but inside, it’s a high-tech ecosystem supporting trillions of digital interactions every day.
When you choose a VPS or dedicated server, you’re also choosing:
-
Power reliability
-
Cooling efficiency
-
Security and uptime guarantees
Now you know what makes it all possible.