How to Build a Scalable Web App: A Developer’s Guide
Want to build a web app that can handle thousands—or even millions—of users without crashing? Scalability is critical for modern applications, ensuring high performance, availability, and efficiency even under heavy traffic.
In this guide, we’ll cover best practices for scalable architecture, database scaling strategies, and load balancing techniques to help developers build highly scalable web applications.
1. What is Scalability in Web Applications?
Scalability refers to a web app’s ability to handle increasing users, traffic, and data without performance degradation. A scalable web app should:
✔ Support more users and transactions without slowing down.
✔ Efficiently use resources (CPU, RAM, database connections).
✔ Scale horizontally or vertically based on demand.
✔ Ensure high availability with minimal downtime.
Types of Scalability:
- Vertical Scaling (Scale Up): Adding more power (CPU, RAM) to an existing server.
- Horizontal Scaling (Scale Out): Adding more servers and distributing the load.
Tip: Horizontal scaling is more cost-effective and fault-tolerant than vertical scaling.
️ 2. Best Practices for Scalable Web App Architecture
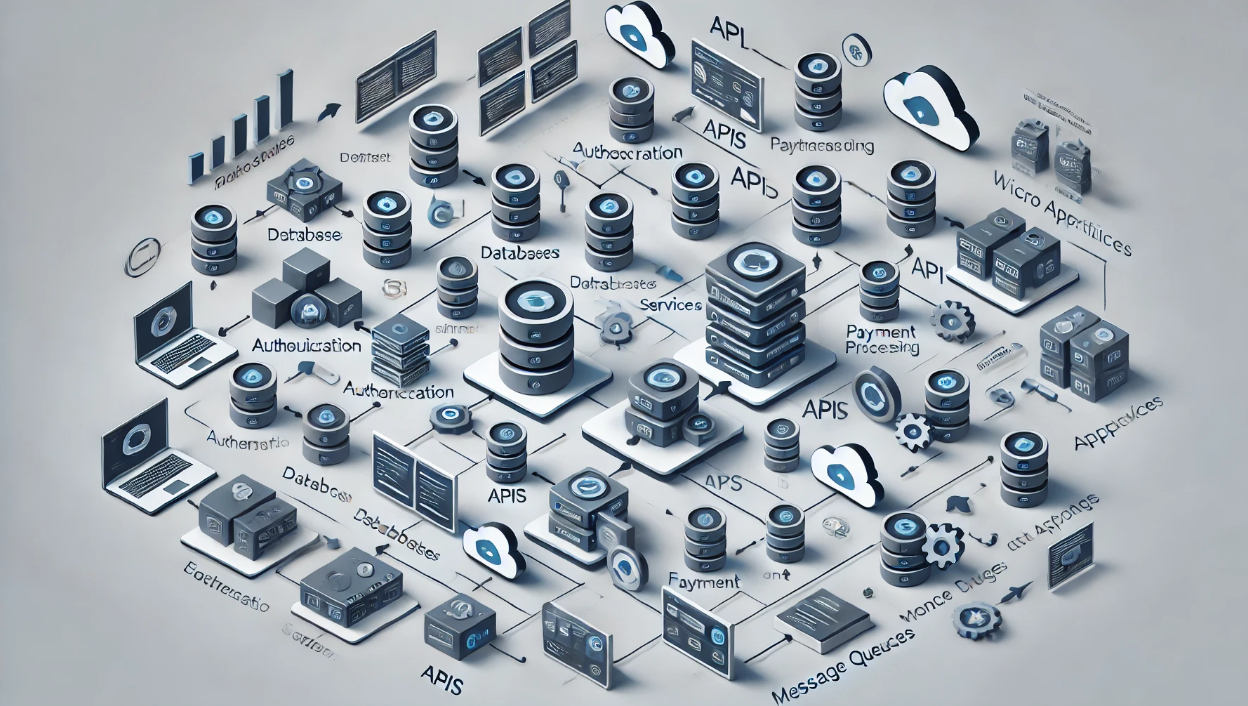
✅ 1. Use a Microservices Architecture
Traditional monolithic applications become hard to scale as they grow. Instead, microservices divide an application into smaller, independent services.
Benefits of Microservices:
✔ Each service scales independently (e.g., user service vs. payment service).
✔ Improves fault tolerance—if one service fails, others keep running.
✔ Enables continuous deployment & faster development cycles.
Tech Stack:
Containerization: Docker, Kubernetes
Service Orchestration: AWS ECS, Kubernetes
Communication: REST API, GraphQL, gRPC
✅ 2. Choose the Right Database Scaling Strategy ️
Databases often become a performance bottleneck as traffic grows. Use scaling techniques to keep queries fast.
Database Scaling Strategies:
✔ Database Replication: Read queries are distributed across read replicas to reduce load.
✔ Database Sharding: Splits data into multiple smaller databases (shards) to improve write speeds.
✔ NoSQL Databases: Use MongoDB, DynamoDB, or Cassandra for handling unstructured data at scale.
✔ Caching: Use Redis or Memcached to store frequently accessed queries in memory.
Tip: Combine replication (for read-heavy apps) and sharding (for write-heavy apps) for maximum scalability.
✅ 3. Implement Load Balancing for High Availability ⚖️
Load balancing ensures traffic is distributed across multiple servers, preventing overload and downtime.
Types of Load Balancing:
✔ Application Load Balancing (Layer 7) – Works at HTTP/HTTPS level (e.g., AWS ALB, Nginx).
✔ Network Load Balancing (Layer 4) – Works at TCP/UDP level (e.g., AWS NLB).
✔ Round Robin DNS Load Balancing – Distributes traffic at the DNS level.
Best Load Balancers:
Nginx – Open-source & widely used for balancing web traffic.
AWS Elastic Load Balancer (ELB) – Scales automatically with cloud apps.
HAProxy – Reliable, high-performance TCP/HTTP load balancer.
✅ 4. Use a CDN to Improve Speed & Reduce Server Load
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) caches static content across multiple locations worldwide.
Best CDNs for Web Apps:
✔ Cloudflare – Free DDoS protection + caching.
✔ AWS CloudFront – Deep integration with AWS services.
✔ Fastly – High-performance edge caching.
Tip: CDNs reduce latency and bandwidth costs while keeping your app fast.
✅ 5. Implement Asynchronous Processing & Queues ⏳
Processing long-running tasks (e.g., emails, payments, data processing) synchronously slows down web apps. Instead, use asynchronous queues.
Best Queueing Systems:
✔ RabbitMQ – Open-source message broker.
✔ Kafka – Best for real-time streaming & event-driven apps.
✔ AWS SQS – Fully managed message queue service.
Example: Instead of processing user sign-ups + email verification in one request, use a queue to send the email asynchronously.
3. Security Best Practices for Scalable Web Apps
A scalable app also needs strong security!
✅ 1. Secure API Endpoints
✔ Use OAuth 2.0 & JWT for authentication.
✔ Rate-limit API requests to prevent DDoS attacks.
✅ 2. Encrypt Data in Transit & at Rest
✔ Use SSL/TLS for HTTPS.
✔ Encrypt sensitive data using AES-256.
✅ 3. Automate Security Patching
✔ Use container scanning tools like Aqua Security.
✔ Automate patching with AWS Systems Manager or Google OS Patch Management.
Tip: Perform regular penetration testing to discover vulnerabilities before hackers do!
4. Monitoring & Performance Optimization Tools
Tracking performance is key to scaling successfully!
Best Monitoring Tools for Web Apps:
✔ New Relic – Application performance monitoring (APM).
✔ Datadog – Cloud infrastructure monitoring.
✔ Prometheus + Grafana – Open-source monitoring stack.
✔ Google Lighthouse – Analyzes page speed & performance.
Tip: Set up automated alerts for high CPU usage, database slowdowns, or traffic spikes to fix issues proactively.
Final Thoughts: Build a Scalable Web App Like a Pro
A scalable web app is designed for speed, resilience, and growth. Follow these steps:
✔ Use Microservices Architecture – Scale components independently.
✔ Scale Databases Efficiently – Use replication, sharding, and caching.
✔ Distribute Traffic with Load Balancing – Prevent server overloads.
✔ Leverage CDNs & Asynchronous Processing – Improve response times.
✔ Secure & Monitor Your App – Protect data and optimize performance.
Ready to scale your web app? Start implementing these best practices today!