In today’s fast-paced IT environments, manual server management is not only time-consuming but also prone to errors.
Ansible, a powerful open-source automation tool, helps simplify server provisioning, configuration, and maintenance—allowing
system administrators and DevOps teams to manage infrastructure effortlessly.
Whether you’re managing a single server or thousands across multiple environments, Ansible’s agentless architecture and simple YAML-based playbooks make automation accessible for teams of all sizes.
What Is Ansible?
Ansible is an open-source IT automation tool developed by Red Hat. It uses declarative YAML files called playbooks to automate infrastructure tasks like:
- ️ Server provisioning
- Configuration management
- Application deployment
- Orchestration of multi-tier environments
⚙️ Key Advantages of Ansible:
- ✅ Agentless: No need to install agents on target servers—it uses SSH.
- Human-readable YAML syntax: No complex coding required.
- ⚡ Idempotent operations: Safe to run repeatedly without unwanted side effects.
- ️ Cross-platform compatibility: Works with Linux, Windows, cloud providers, and network devices.
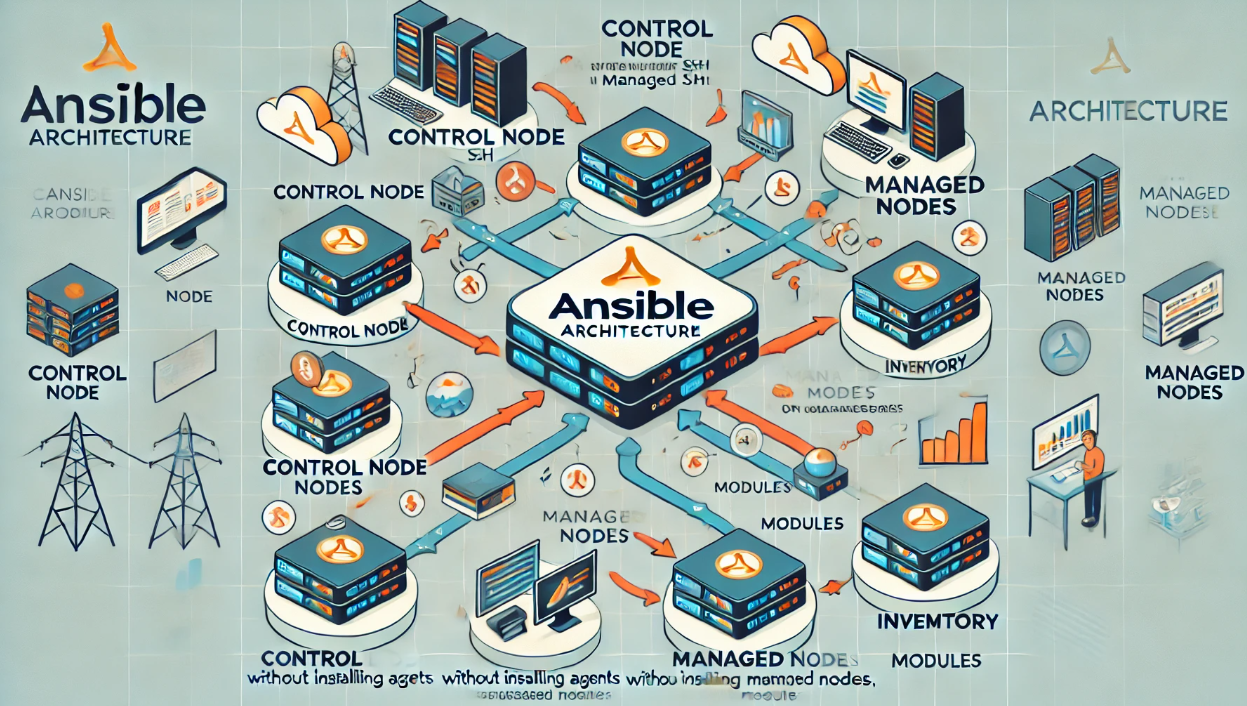
How Ansible Works: The Core Components
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Control Node | The machine running Ansible to manage target servers. |
| Managed Nodes | Target servers where tasks are executed—no agent needed. |
| Inventory | A file listing managed nodes (IP addresses or hostnames). |
| Modules | Pre-built units of automation logic for various tasks. |
| Playbooks | YAML files that define tasks and workflows. |
| Tasks | Actions performed on target servers (e.g., installing software). |
| Roles | Reusable playbook components for better organization. |
️ Getting Started with Ansible
️ 1. Install Ansible
# For Ubuntu/Debian
sudo apt update
sudo apt install ansible -y
# Verify installation
ansible --version
Output Example:
ansible 2.14.0
python version = 3.10.6
2. Set Up the Inventory File
Create an inventory file to define your target servers:
# Create an inventory file
nano /etc/ansible/hosts
Sample Inventory File:
[web_servers]
192.168.1.101
192.168.1.102
[db_servers]
192.168.1.201
[all:vars]
ansible_user=admin
ansible_ssh_private_key_file=/home/admin/.ssh/id_rsa
3. Run Your First Ansible Command
Use the following command to test connectivity:
ansible all -m ping
Expected Output:
192.168.1.101 | SUCCESS => {
"ping": "pong"
}
⚙️ Automating Server Provisioning with Ansible
Server provisioning involves:
- Installing operating systems
- Configuring SSH access
- ️ Setting up necessary software
️ Playbook Example: Provision a Web Server
---
- name: Provision Web Server
hosts: web_servers
become: true
tasks:
- name: Update package cache
apt:
update_cache: yes
- name: Install Nginx
apt:
name: nginx
state: present
- name: Enable and start Nginx service
systemd:
name: nginx
state: started
enabled: yes
- name: Allow HTTP traffic through firewall
ufw:
rule: allow
port: 80
proto: tcp
Run the playbook:
ansible-playbook provision_web_server.yml
Automating Server Configuration with Ansible
️ Playbook Example: Configure SSH Security
---
- name: Secure SSH Configuration
hosts: all
become: true
tasks:
- name: Disable root login
lineinfile:
path: /etc/ssh/sshd_config
regexp: '^PermitRootLogin'
line: 'PermitRootLogin no'
backup: yes
- name: Restart SSH service
systemd:
name: ssh
state: restarted
Run the playbook:
ansible-playbook configure_ssh.yml
Automating Server Maintenance with Ansible
️ Playbook Example: Automate System Updates
---
- name: Perform System Maintenance
hosts: all
become: true
tasks:
- name: Update system packages
apt:
update_cache: yes
upgrade: dist
- name: Remove unnecessary packages
apt:
autoremove: yes
- name: Clean up APT cache
apt:
autoclean: yes
- name: Reboot servers if needed
command: shutdown -r now
async: 1
poll: 0
ignore_errors: yes
Run the playbook:
ansible-playbook maintenance.yml
Advanced Ansible Features for Server Automation
️ 1. Ansible Roles for Modular Playbooks
ansible-galaxy init roles/nginx_setup
2. Ansible Vault for Secure Data
# Encrypt a Password File:
ansible-vault encrypt secrets.yml
# Usage in Playbooks:
- name: Deploy App with Secret Keys
hosts: web_servers
vars_files:
- secrets.yml
3. Ansible AWX/Tower for Web-Based Management
AWX provides a web interface for:
– Task visualization
– Job scheduling
– ️ Centralized inventory management
Conclusion: Ansible as Your Server Automation Ally
Ansible simplifies server management by automating provisioning, configuration, and maintenance—reducing manual effort and human errors.
Key Takeaways:
- ️ Agentless architecture makes it easy to deploy across large infrastructure.
- Declarative playbooks ensure reproducible configurations.
- Built-in security features like Ansible Vault protect sensitive data.
- Continuous automation saves time and resources for mission-critical tasks.
Start automating today and empower your infrastructure with Ansible!